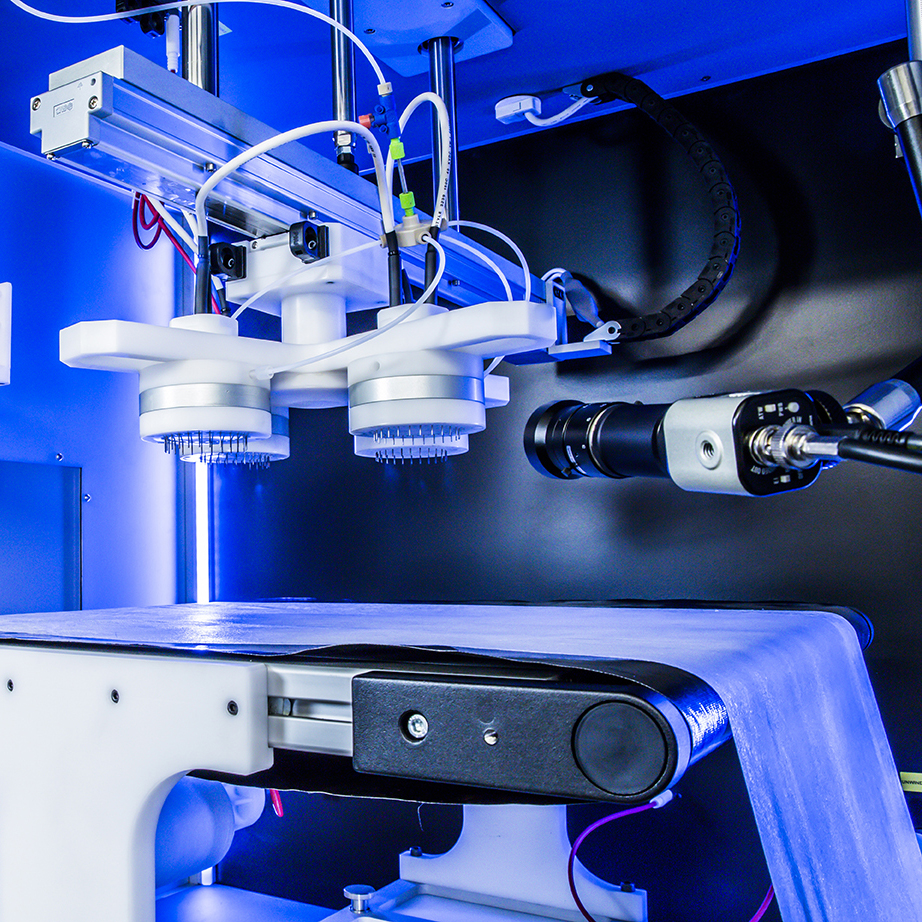
Electrospin Services

Electrostatic spinning or electrospinning is a fiber production method that uses electrical power to stretch charged filaments of polymer solutions or polymer melts to nanoscale fiber diameters. Electrospinning has both electro-atomization and conventional dry spinning properties of fibers.
Since electrospinning technology can be used to prepare highly porous nanofibers from different materials, and can move from random spinning to oriented random weaving, from organic materials to inorganic materials and their composites, and has multifunctional properties such as drug-carrying, cell-carrying, growth factor-carrying, and gene-carrying, it can play a striking role in various fields of regenerative medicine and related biomedical engineering.